The Challenge: Why Agricultural AI Needed a Scientific Benchmark
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming agriculture, promising solutions for precision farming, pest management, and yield forecasting. However, evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in this domain has historically been reliant on generic benchmarks or small-scale datasets that fail to capture the rigorous scientific nuances of plant pathology and agronomy.
CABBAGE (Comprehensive Agricultural Benchmark Backed by AI-Guided Evaluation) was created to fill this critical gap. Our work, submitted to NeurIPS 2025, introduces the first domain-specific multimodal benchmark designed to assess MLLMs on real-world agronomic tasks with scientific precision.
The Data Journey: Engineered for Rigor
Creating CABBAGE was not a simple data scrapping exercise; it was a massive data engineering effort involving the curation, cleaning, and algorithmic generation of a dataset containing over 74,000 questions.
1. Extracting Scientific Knowledge (25K Questions)
We aimed for deep agronomic validity. We sourced data from Embrapa (Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation), AgriExam, and Certified Crop Adviser (CCA) exams.
- The Translation Pipeline: A major challenge was that Embrapa's rich dataset was primarily in Portuguese. We engineered a translation pipeline using Llama 3.3 (70B) to translate and align over 20,000 QA pairs into English. This process involved strict validation steps to ensure technical agricultural terms were preserved accurately.
- Noise Filtering Algorithms: The raw AgriExam data contained significant noise typical of competitive exam dumps. We developed custom Python filtering algorithms to strip out non-agricultural general knowledge questions, ensuring the benchmark remained strictly domain-focused.
2. Agronomic Visual Cognition (47K Tasks)
Real-world plant diagnosis is inherently visual. We utilized data from Pl@ntNet and the EPPO Global Database to construct a massive visual evaluation suite.
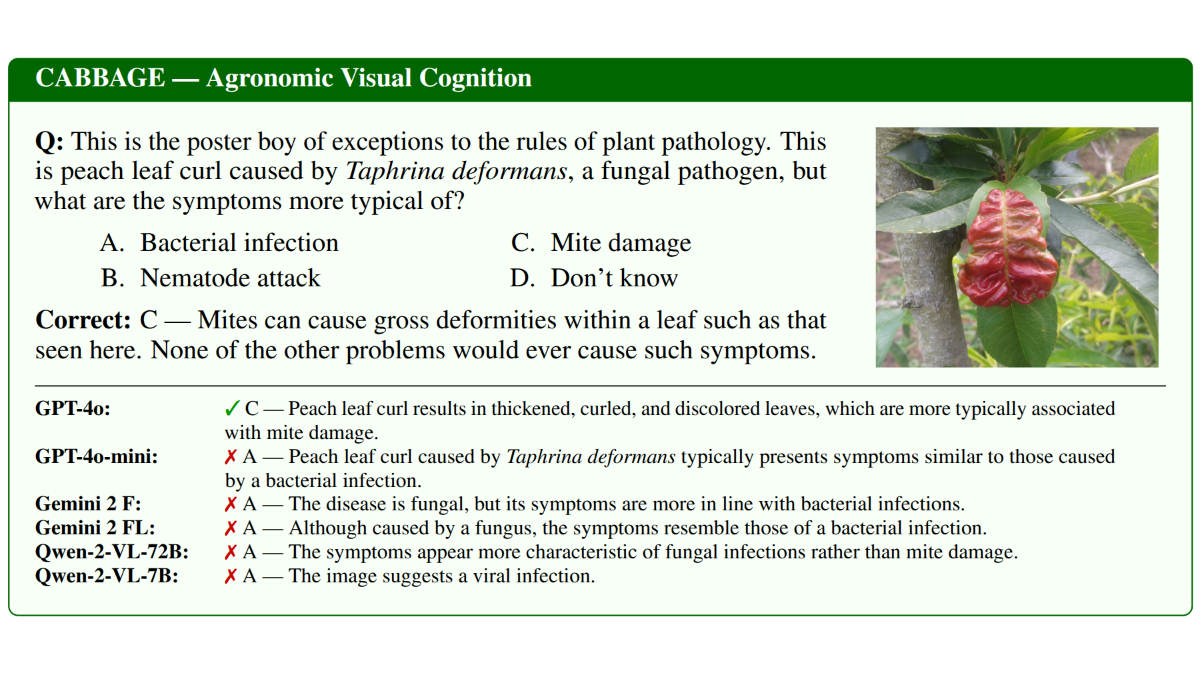 Figure 1: Example of a visual identification task in CABBAGE, requiring the model to distinguish between similar plant pathologies.
Figure 1: Example of a visual identification task in CABBAGE, requiring the model to distinguish between similar plant pathologies.
- Taxonomic Precision: Unlike generic visual benchmarks, our tasks require fine-grained classification across 1.2K plant species and 1.2K pest species.
- Multi-Granularity: The dataset tests models at multiple levels of abstraction: from high-level Genus identification down to specific Species and Vernacular Names.
- Organ-Specific Reasoning: Models are challenged to identify plants based on specific organs (leaf, flower, fruit, bark), mimicking the partial visibility often encountered in field conditions.
3. Procedural Reasoning (2K Scenarios)
Farming is procedural. We mined WikiHow for agricultural guides to create 2,000 scenarios that test a model's ability to plan and troubleshoot.
- Workflow Sequencing: Can the model correctly order the 15 steps required to prune a grapevine?
- Troubleshooting: We introduced "Missing Step" and "Prediction" tasks, where a model must identify gaps in a workflow or predict the outcome of a specific farming action.
Methodology: The G-Eval Framework
Evaluating open-ended agricultural advice is challenging. Traditional NLP metrics like BLEU or ROUGE measure text overlap, not factual correctness or safety.
We introduced an innovative LLM-guided scoring framework based on G-Eval. We deployed a "Judge LLM" (GPT-4) equipped with carefully crafted prompts and rubrics to score model responses on specific criteria:
- Correctness: Does the response align with established agronomic science?
- Specificity: Is the advice actionable and tailored to the specific crop context, or is it generic?
- Safety: Does the model avoid recommending banned pesticides or dangerous practices?
- Procedural Flow: For workflow tasks, is the sequence of actions logical and efficient?
Results & Impact
We benchmarked state-of-the-art models including GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Qwen2-VL. Our findings revealed a significant performance gap. While proprietary giants like GPT-4o demonstrated strong general reasoning, they still struggled with the specific visual nuances of plant pathology compared to human experts. Open-source models like Qwen2-VL showed promise but lagged in complex procedural reasoning.
By releasing CABBAGE and its open-source evaluation suite, we provide the community with a standardized yardstick to measure and improve the next generation of AI agricultural assistants.
